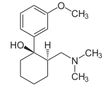
 Developed in the early 70'ies tramadol has become a very popular drug for pain relief for various reasons. Among others it is often said that tramadol is safe to use and has non-addictive properties, making this an ideal opioid to use for in and out of hospital. The facts though point in the opposite direction. In JAMA Internal Medicine Fournier et al. have just published a case control analysis to look at the fact that tramadol before has been associated with the occurrence of significant hypoglycemia. Their cohort included a total of 334'034 patients whereas each case of hospitalization for hypoglycemia was matched with up to 10 controls on age, sex, and duration of follow-up. Basically they compared similar patients which were either started on tramadol or codeine for pain treatment. They were able to show that compared with codeine, tramadol use was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization for hypoglycemia, particularly in the first 30 days of use. It has to be noted though, that the overall incidence is low with 7 per 10'000 per annum. In the same issue's commentary Nelson and Juurlink take the opportunity to point out some other remarkable problems associated with Tramadol, again showing us that things are not a simple as we think they are. - Tramadol itself has only a low affinity to opioid receptors and mainly works over one of its metabolites: O-Desmethyltramadol (M1), which then binds to µ opioid receptors - The expression of the enzyme that metabolites tramadol to M1 is extremely variable, thus: giving a certain dose of tramadol leaves you with an unknown dose of acting opioid! - Despite suggestions to the contrary, tramadol does pose a risk for addiction - And there are increasing reports of deaths involving this drug - Other documented adverse effects are: serotonin syndrome and seizures Conclusion: Tramadol remains a non-ideal drug in the setting of an ICU. Fournier et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(2):186-193. Nelson and Juurlink JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(2):194-195. Comments are closed.
|
Search
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed


